(AAAI2023)Masked Autoencoders for Occlusion-aware Visual Learners
 A Unified TinyML System for Multi-modal Edge Intelligence and Real-time Visual Perception
A Unified TinyML System for Multi-modal Edge Intelligence and Real-time Visual PerceptionResearch Opportunity 5: Masked Autoencoders for Occlusion-aware Visual Learners
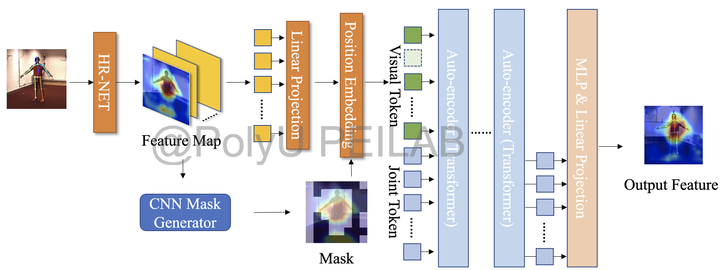
Illustration: Recent years have witnessed learning-based video perception algorithms getting popular in more scenarios with occlusions, where invisible areas for perception objects significantly affect accuracy. Existing methods mainly use convolutional neural networks as the backbone and get limited local features to recover the occluded part. Such an anti-occlusion pipeline often suffers from the challenges of self-occlusion scenery, where similar parts of occluders and occludes are ambiguous. In this case, we need to design a masked visual autoencoder for image processing and video streaming, which recovers occluded regions by extracting deep spatial information at a higher semantic level. This autoencoder can get better details inferred from global self-attention and thus improves accuracy. The gist is to train the autoencoder to extract key-point information from the key patches that are manually masked in a self-supervised manner to simulate the occlusion in video streaming. To choose the patches that should be masked, we design a high-capacity learnable gate that can extract contrastive representation, i.e., distinguish important feature regions and background regions, to generate a binary mask by randomly choosing a part of feature patches. We also propose an end-to-end pipeline for training and inference, which can effectively reduce the dependency of annotated occluded datasets and can be further applied to other visual tasks. This pipeline can obtain a great computation saving with much fewer annotated datasets, and hold a higher runtime performance over the SOTA ViT methods.