(ICML2024) Easing Concept Bleeding in Diffusion via Entity Localization and Anchoring
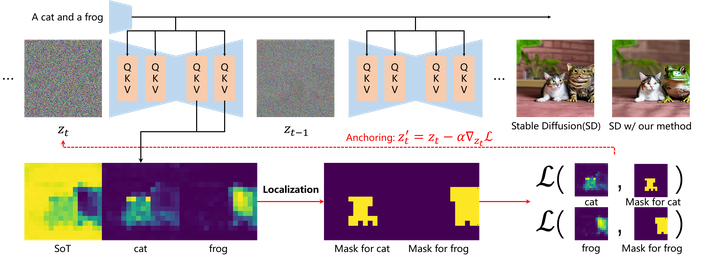
When generating multi-entity scenes, stable diffusion and its derivative models frequently encounter issues of entity overlap or fusion, primarily due to cross-attention leakage. To mitigate these challenges, we propose performing differentiation and binarization on cross-attention maps to accurately locate entities within non-overlapping areas. Additionally, we suggest designing a loss function that constrains entities to these specified areas. Finally, we recommend anchoring entities to their designated areas by slightly updating the latent representation.
Recent diffusion models have manifested extraordinary capabilities in generating high-quality, diverse, and innovative images guided by textual prompts. Nevertheless, these state-of-the-art models may encounter the challenge of concept bleeding when generating images with multiple entities or attributes in the prompt, leading to the unanticipated merging or overlapping of distinct objects in the synthesized result. The current work exploits auxiliary networks to produce mask-constrained regions for entities, necessitating the training of an object detection network. In this paper, we investigate the bleeding reason and find that the crossattention map associated with a specific entity or attribute tends to extend beyond its intended focus, encompassing the background or other unrelated objects and thereby acting as the primary source of concept bleeding. Motivated by this, we propose Entity Localization and Anchoring (ELA) to drive the entity to concentrate on the expected region accurately during inference, eliminating the necessity for training. Specifically, we initially identify the region corresponding to each entity and subsequently employ a tailored loss function to anchor entities within their designated positioning areas. Extensive experiments demonstrate its superior capability in precisely generating multiple objects as specified in the textual prompts.